Longfei Li, Qinyong Dai, Yating Li, Mengjiao Pei, Minoru Osada, Yun Li"Autonomous Light Intensity Adaptation in an Energy-Efficient Retinomorphic Organic Ferroelectric Neuristor, Adv. Optical Mater.2024, 2303172
DOI: 10.1002/adom.202303172
Abstract
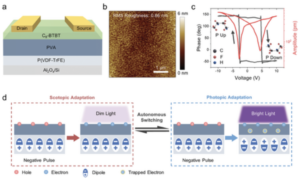
In biological visual systems, retina with bidirectional photoresponse can adapt to variable environments and modulate their photosensitivity dependent on illumination conditions in an energy-efficient way. However, to emulate the visual functionality, current systems still require a sustained power supply and manipulate the electrical stimulation manually according to light intensity, thus incurring high energy consumption and the lack of autonomous adaptive function. Herein, an organic ferroelectric neuristor emulating the visual self-adaptation function of retina is introduced. Such autonomous adaptive behavior of device originates from the trap-assisted ferroelectric polarization reversal under light illumination. It allows to realize bidirectional photoresponse in a single device according to light intensity, thus breaking through the limitation of commonly adaptive devices with single photoresponse mechanisms. In particular, only a single gate voltage pulse with an ultralow energy consumption of ≈34 pJ is required to accomplish the adaptation behavior, endowing the visual perception with high autonomy and power efficiency. Finally, the application potential of the neuristor in image pre-processing and recognition under bright and dim light conditions is demonstrated. Therefore, this work opens up a path for the development of retina-like visual systems with highly energy efficient.
