Masanari Shimada, Yan Li, Makoto Kobayashi, Eisuke Yamamoto, Ruben Canton-Vitoria, Minoru Osada*
Abstract
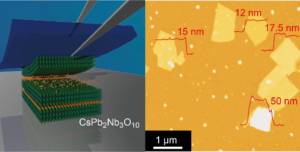
Mechanical exfoliation of layered materials is one of the most effective methods for obtaining two-dimensional (2D) nanosheets. However, this approach is still limited to van der Waals (vdW) layered materials, where interlayer interactions are governed by weak vdW forces. In this study, we used a layered perovskite ferroelectric (CsPb2Nb3O10) as a model system to explore the mechanical exfoliation behavior of ionically bonded non-vdW layered materials. Due to the relatively weak out-of-plane bonds involving the interlayer Cs⁺ ions, CsPb2Nb3O10 could be cleaved into ultrathin sheets with thicknesses ranging from 7.5 nm to 50 nm. Using piezoresponse force microscopy, we investigated the thickness-dependent ferroelectric properties of CsPb2Nb3O10 nanosheets.
